Hypermobility
 Hypermobility is the term used to describe overly mobile joints. It is a normal variation of the way our joints (capsule and ligaments) are put together. It is caused by the protein collagen (which makes up our connective tissue) being more flexible than usual and occurs in 10-20% of the population. The degree of compliance, or stretchiness, in connective tissue is genetically predetermined. Children with hypermobility will usually have a parent or other close relative with hypermobility.
Hypermobility is the term used to describe overly mobile joints. It is a normal variation of the way our joints (capsule and ligaments) are put together. It is caused by the protein collagen (which makes up our connective tissue) being more flexible than usual and occurs in 10-20% of the population. The degree of compliance, or stretchiness, in connective tissue is genetically predetermined. Children with hypermobility will usually have a parent or other close relative with hypermobility.
Of course, like a lot of conditions, hypermobility varies on a spectrum of different severities. In this case we are referring to Generalised Joint Hypermobility (GJH) which has benign or non-life threatening symptoms. At the other end of the spectrum are conditions such as Marfans or Elhers Danlos Syndrome which can have more serious complications.
How do I tell if I am hypermobile?
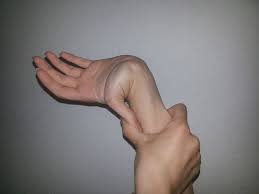
If an individual has 5 or more joints that are more flexible than usual then he or she can be said to have GJH. The movements are:
- Finger extension
- Wrist flexion
- Elbow extension
- Hip rotation
- Knee extension
- Ankle flexion
What are the effects of Generalised Joint Hypermobility?
Some of the effects may be:
- Poor posture
- Muscle weakness
- Poor endurance, difficulty with prolonged exercise
- Loose joints but tight muscles
- Flat feet
- Generally more prone to injury
Most ballet dancers and gymnasts will have a degree of hypermobility thus demonstrating that it is also possible to be hypermobile AND be fit, strong and active.
How can physiotherapy help?
- Assist with core stability and posture
- Soft tissue release of muscles
- Provide an exercise program to increase muscle strength and endurance thus supporting the joints eg. Scapular stability and rotator cuff exercises to support the hypermobile shoulder
- Advice on stretches for tight muscles
- Fitting of orthotic support for flat feet
- Provide advice on factors which may reduce the worsening of symptoms eg, choosing appropriate sports and exercise programs
